defensive copying 的为什么和怎么做
defensive copying(保护性拷贝)是在软件实现中常会用到的概念,这篇博客主要介绍为什么需要 defensive copy 和如何实现 defensive copying。
参考资料:
为什么
A class may have a mutable object as a field. There are two possible cases for how the state of a mutable object field can change:
- its state can be changed only by the native class - the native class creates the mutable object field, and is the only class which is directly aware of its existence
- its state can be changed both by the native class and by its callers - the native class simply points to a mutable object which was created elsewhere
Both cases are valid design choices, but you must be aware of which one is appropriate for each case.
If the mutable object field’s state should be changed only by the native class, then a defensive copy of the mutable object must be made any time it’s passed into (constructors and set methods) or out of (get methods) the class. If this is not done, then it’s simple for the caller to break encapsulation, by changing the state of an object which is simultaneously visible to both the class and its caller.
参数引用
1 | class Person { |
返回值引用
1 | EmailMessage msg = ... |
怎么做
defensive copying 有时候也被叫做 “object copying”,从这个名字可以看出它的做法——拷贝一个对象。
参数保护
Because Java’s standard collection types may be mutable, the immutable Person type must protect itself from callers who would modify the favoriteMovies list after creating a new Person:
1 | public Person(String name, List<String> favoriteMovies) { |
The Person class must make a defensive copy of the favoriteMovies collection. By doing so, the Person class captures the state of the favoriteMovies list as it existed when the Person was created.
返回值保护
1 | public Date getDate() { |
完整示例类
1 | import java.util.Date; |
关于深浅拷贝的解释
Shallow copy
One method of copying an object is the shallow copy. In that case a new object B is created, and the fields values of A are copied over to B. This is also known as a field-by-field copy, field-for-field copy, or field copy. If the field value is a reference to an object (e.g., a memory address) it copies the reference, hence referring to the same object as A does, and if the field value is a primitive type it copies the value of the primitive type. In languages without primitive types (where everything is an object), all fields of the copy B are references to the same objects as the fields of original A. The referenced objects are thus shared, so if one of these objects is modified (from A or B), the change is visible in the other. Shallow copies are simple and typically cheap, as they can be usually implemented by simply copying the bits exactly.
Deep copy
A deep copy in progress.

A deep copy having been completed.
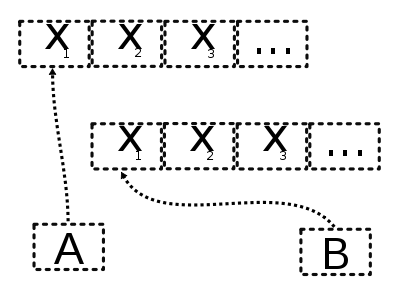
An alternative is a deep copy, meaning that fields are dereferenced: rather than references to objects being copied, new copy objects are created for any referenced objects, and references to these placed in B. The result is different from the result a shallow copy gives in that the objects referenced by the copy B are distinct from those referenced by A, and independent. Deep copies are more expensive, due to needing to create additional objects, and can be substantially more complicated, due to references possibly forming a complicated graph.
Deep copy is a process in which the copying process occurs recursively. It means first constructing a new collection object and then recursively populating it with copies of the child objects found in the original. In case of deep copy, a copy of object is copied in other object. It means that any changes made to a copy of object do not reflect in the original object. In python, this is implemented using “deep copy()” function.
总结
传递引用要谨慎,若该类中的某个字段是mutable类型,但需求为不能更改,那么应该在字段前加上final修饰,且在构造器和getter、setter中传送的应该是该字段的拷贝。
Defensive copying helps encapsulation as it mitigates escape of fields through the getters methods. Defensive copying creates a copy every time and thus you can end up with too many copying of something. This can strain the memory management (the garbage collector) and can have a negative effects on the whole application performance. With that said, it is quite effective and simple to implement. Prevention is better than cure, but in cases where we cannot change the types, defensive copying can step in and save the day.